One essential feature of every computer programming language is the ability to execute a piece of code repeatedly. It saves a lot of time and also reduces the lines of code in a program. Bash programming enables users to run a task again and again by use of Loops. In this article, we will look at the For Loop statement.
A For Loop statement is used to execute a series of commands until a particular condition becomes false. For example, you can use it to run a Linux command five times or use it to read and process files on the systems until reaching a particular condition.
Bash For Loop command
The For Loop in Bash programming comes in two different syntaxes:
- The For In Loop
for item in (list) do command_one command_two ... done
In the above For In Loop syntax, there are four keywords – for, in, do, and done. The list refers to the values in the ‘list.’ Item is a variable name that is no keyword in Bash programming language.
When we run the program, it will execute the command depending on the number of items in the ‘list.’ Therefore, if the list contains five figures, (1 2 3 4 5), the command is executed five times.
In every iteration, the value in the list is stored in the item variable and used in the program body.
- The For Loop with syntax like that of C programming language
for (( expression_1; expression_2; expression_3)) do command_one command_two ... done
With the above For Loop statement, if you are a C, C++, or Java developer, you should be familiar with the syntax. ‘expression_1 stands for initialization, expression_2 stands for condition, and expression_3 stands for updation.
When we run the program, ‘expression_1’ is evaluated before performing the first iteration initializing the variable values for the For Loop.
The program body is executed until expression_2 is TRUE. The program body here refers to the commands between the do and done keywords. Now, after every iteration of the program, expression_3 is evaluated.
Having grasped that, let’s look at some Bash For Loop examples you can utilize in your everyday activities working with Linux systems. We will write scripts and execute them in the terminal. Note, all Bash scripts use the ‘.sh.’ extension.
Use For Loop to print a series of Strings
You can use a For In Loop to print a series of strings. Take a look at the code below. We already have the three files used in the program in our working directory. That is ‘testFile1’, ‘testFile2’, and ‘testFile3’.
#!/bin/bash for item in testFile1 testFile2 testFile3 do cat $item echo "Done with file $item" echo done
The output is:
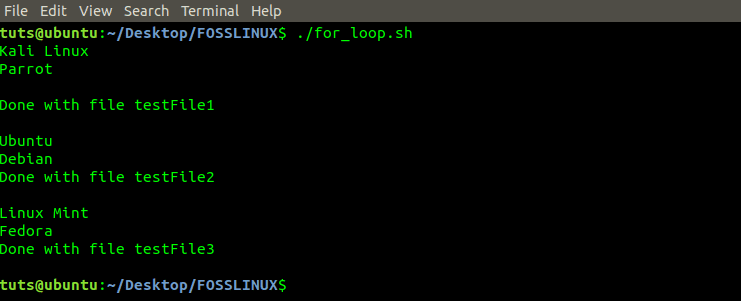
For Loop Program
The program above lists the contents of the file specified in the list. That is, testFile1, testFile2, and testFile3. The ‘cat’ command is a Linux utility used to display the contents of a file.
Therefore, the program loops through the files starting with ‘testFile1’, execute the ‘cat’ command on it before printing the statement ‘done with testFilee’ and iterates to the next file.
After iterating through all the files in the list, the program terminates automatically.
‘For In Loop’ with Array elements to Backup Files
You can use a For In Loop to iterate elements in an array. Take a look at the code below.
#!/bin/bash
Files=('testFile1' 'testFile2' 'testFile3')
for item in "${Files[@]}";
do
cp $item{,.bak}
echo "Created a backup of $item"
done
The output is as shown below.
For Loop Image
The program above uses cp command to create backups of files in the array. As it iterates through every file, it creates a backup of the data and prints the ‘Created Backup message’ before moving to the next item in the array.
‘For In Loop’ with Range
You can iterate over a range of numbers. For example, you wish to iterate between digits 1 – 100. Writing all these numbers in your program will make the code quite much. We can solve this by use of ranges. Take a look at the code below.
#!/bin/bash
for i in {0..50}
do
echo "COUNT: $i"
done
The output should be as shown below.
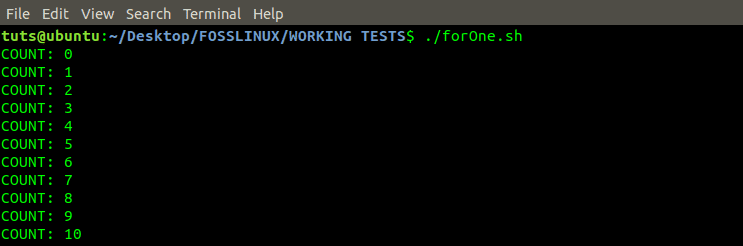
For Loop Program
From the above output, we see the program has printed numbers 1 – 50. It is because we gave it a range of 1 – 50 digits.
Suppose you want to create a range that skips a certain number of digits before printing an output. Then we will need to include a third parameter in the range syntax. See the code below.
#!/bin/bash
for i in {0..100..10}
do
echo "COUNT: $i"
done
The output should be as shown below.
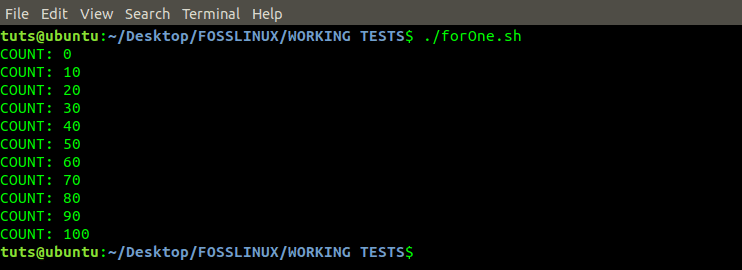
For Loop Program
The output should be as shown below.
From the image above, we see that the program printed numbers 0 – 100 but skipping Ten (10) digits in every iteration.
‘For Loop’ with C programming Syntax
Having looked at several examples with the ‘For In Loop,’ let’s look at the other For Loop Syntax. It contains an Initialization expression that initializes the Loop, a Condition expression that determines the execution of the program, and an Increment expression that updates the variable value.
Take a look at the code below.
#!/bin/bash for (( i=5; i>=1; i-- )) do echo "COUNT: $i" done
The output should be as shown below.
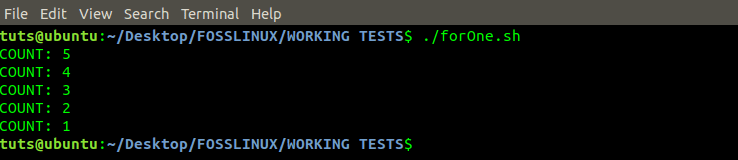
For Loop Program
Create an Infinite Loop with For Loop
To create an infinite loop in Bash, we will use the C programming syntax. See the code below.
#!/bin/bash for (( ; ; )) do echo "Use Ctrl+C to terminate the loop." echo "Starting Infinite Loop..." done
The output should be as shown below.
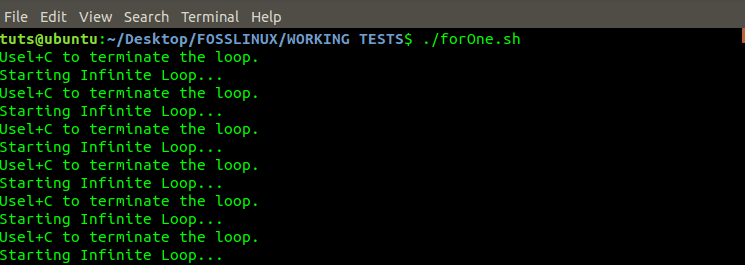
For Loop Infinite Program
To get out of an infinite loop, press Ctrl + C to cancel the process.
Break and Continue statements in a ‘For Loop’
In programming, the Break and Continue statements control the execution of a program. The Break statement terminates the program and gets out of the Loop. The Continue statement, on the other hand, forces the next iteration of the program to take place.
-
The Break Statement
Let’s look at the program below, which makes use of the Break statement.
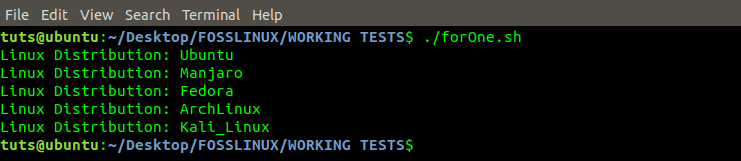
#!/bin/bash for distro in Ubuntu Manjaro Debian Fedora Kali ArchLinux do if [[ "$distro" == 'kali' ]]; then break fi echo "Linux_distribution: $distro" done
The output should be as shown below.
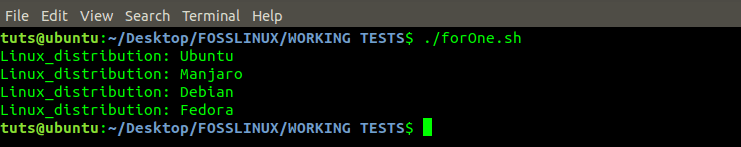
For Loop Program
From the image above, we see that ‘Kali’ was not printed in the output. It’s because we gave an ‘If Condition’ that checked to see the value held by the variable ‘distro.’ If the value was ‘Kali,’ the ‘break’ statement was executed and terminated the Loop.
As you can see, ArchLinux was not printed in the output because the break statement ended the program.
The Continue statement
Unlike the Break statement, the Continue statement terminates the program on that part but forces the next iteration of the program to run.
Take a look at the code below.
#!/bin/bash for distro in Ubuntu Manjaro Debian Fedora Kali ArchLinux do if [[ "$distro" == 'Kali' ]]; then continue fi echo "Linux_distribution: $distro" done
The output should be as shown below.
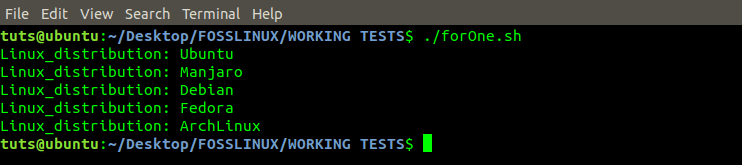
For Loop Program
From the image above, we see that ‘Kali’ was not printed in the output. It’s because we gave an ‘If Condition’ that checked to see the value held by the variable ‘distro.’ If the value was ‘Kali,’ the ‘continue’ statement was executed. It terminated the Loop at this point but forced the execution of the next part of the program.
As you can see, ‘Kali’ was not printed in the output while ‘ArchLinux’ was. The Continue statement forced the execution of the next part of the program.
More Practical Bash Programs using the For Loop
Having looked at several Bash programs using the ‘For Loop’ statement, let’s look at real-life examples you can use to manage your Linux systems.
- A Bash program to convert MP3 files to WAV
In this program, you will need the MPG123 tool installed in your system. The code below looks for any file with the extension ‘.mp3.’ and converts it to a ‘.wav.’ file using the ‘mpg123’ tool.
#!/bin/bash for item in ./*.mp3 do mpg123 -w music.wav $item.mp3 done
From the image below, we see we converted ‘Audio.mp3’ to ‘Music.wav.’
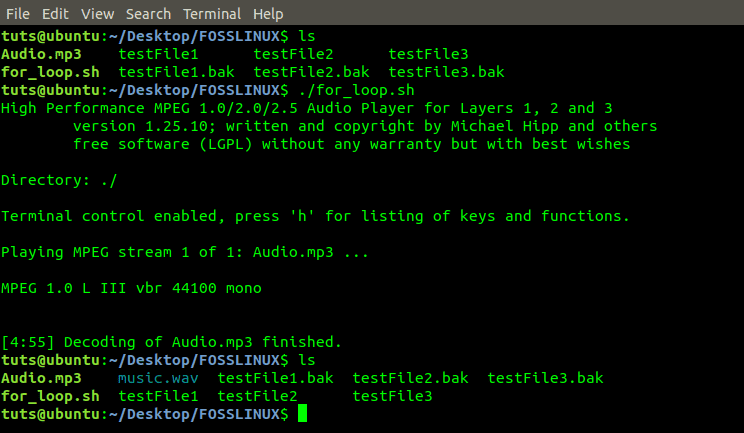
Convert Mp3 file to wav
- ‘For Loop’ program to check whether firefox.desktop files exist.
The program below will iterate through all files present in the applications/ directory and give an output of whether firefox.desktop is present.
#!/bin/bash
for item in /usr/share/applications/*
do
if [ "${item}" == "/usr/share/applications/firefox.desktop" ]
then
echo "Firefox.Desktop is present in the applications directory";
fi
done
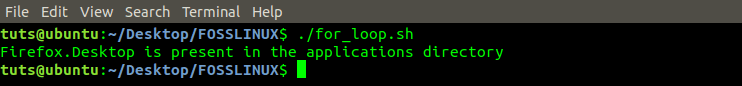
For loop Program
Conclusion
Now that you have learned using the For Loop statement in Bash programming, create programs to automate various tasks in your Linux systems. If you found this article helpful, feel free to share the link with your friends.


1 comment
Thank you for this examples