Over the years, Linux Mint has become an in-demand operating system for personal computers. As you would already know, one of the key components of any modern operating system is its sound system, and Linux Mint uses PulseAudio as its default sound server. PulseAudio is a powerful and versatile server that allows for flexible management of audio sources and outputs.
In this article, we will discuss how to configure PulseAudio in Linux Mint, including installation, setting default input/output devices, managing volume levels, and advanced configurations. While Linux Mint comes with a wide range of pre-installed applications, there may be times when you need to install additional software. This is where Flatpak, a universal packaging format, comes in. Learn how to install and use Flatpak on Linux Mint.
What is PulseAudio?
PulseAudio is a sound server that provides a way to manage and control audio sources and outputs on Linux systems, including Linux Mint. It was designed to allow multiple applications to share audio hardware and to provide a flexible, centralized way of managing audio on Linux systems.
PulseAudio in Linux Mint
The purpose of PulseAudio is to provide a unified audio experience for users, allowing them to easily control and manage audio sources and outputs from a single interface. It can control the volume of individual applications, route audio to different outputs, and even provide sound effects or DSP processing.
PulseAudio works by creating a virtual audio device that applications can connect to. This virtual device can be configured to use one or more physical audio devices, allowing multiple applications to share the same hardware. PulseAudio also provides a way to manage and control audio streams, allowing users to adjust volume levels and balance between different inputs.
Controlling audio streams
In Linux Mint, PulseAudio is the default sound server, providing a stable and flexible way to manage audio. It is used by default in many applications and can be configured through a graphical interface or the command line. Understanding how to configure PulseAudio in Linux Mint is essential for getting the most out of your system and ensuring a smooth and reliable audio experience.
Installing PulseAudio on Linux Mint
You can install PulseAudio on Linux Mint through the command line as well as the graphical interface. Open the terminal window and run the following command:
sudo apt-get install pulseaudio
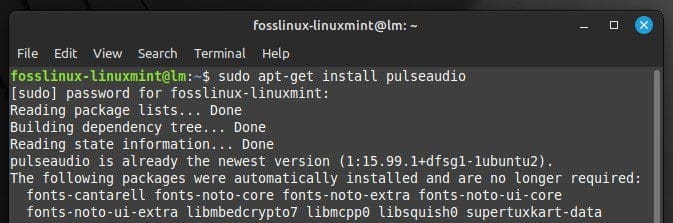
Installing PulseAudio on LinuxMint
It downloads and installs the PulseAudio package along with any necessary dependencies. Once the installation is complete, you may need to restart your system for the changes to take effect.
Restarting Linux Mint
Alternatively, PulseAudio can also be installed through the graphical interface. To do so, open the “Software Manager” and search for “PulseAudio”. Select the package from the results and click on the “Install” button to initiate the installation process. The Software Manager will handle the installation, and you will be prompted to enter your password to authorize only in the beginning.
Installing PulseAudio through the software manager
Once PulseAudio has been installed, it will automatically start up and run in the background. You can confirm that PulseAudio is running by opening the “PulseAudio Volume Control” application, which is available in the “Sound & Video” category of the Mint Menu. This application provides a separate interface for configuring PulseAudio settings and devices.
Configuring default output devices
PulseAudio allows you to set a default output device for audio playback, the device that audio will be routed to by default. To configure the default output device, you first need to identify the available output devices on your system.
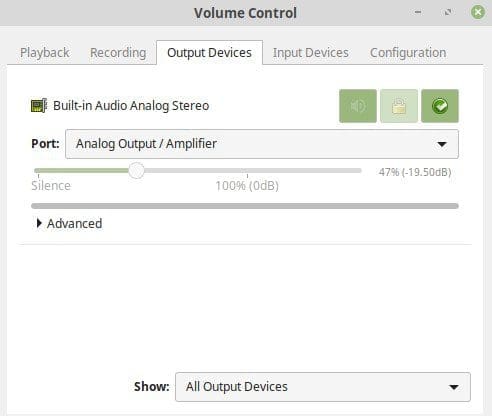
Open the “PulseAudio Volume Control” application to identify the available output devices. Click on the “Output Devices” tab to view a list of available output devices. You should see a list of devices such as “Speakers”, “Headphones”, “HDMI Output”, or other audio peripherals that are connected to your system.
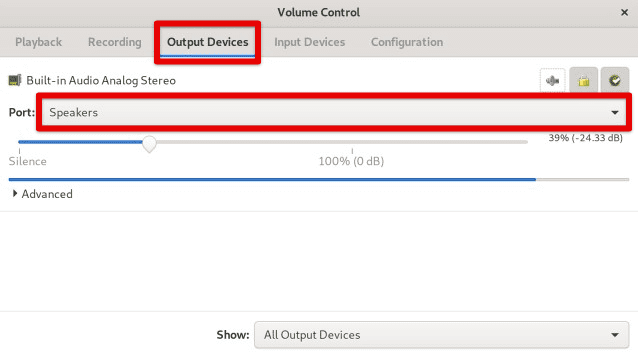
PulseAudio volume control output devices
To set the default output device, simply click on the green checkmark icon next to the device you want to set as default. This will mark the device as the default output, and audio will be automatically routed to this device unless specified otherwise. You can also adjust each device’s volume level and balance with the provided sliders.
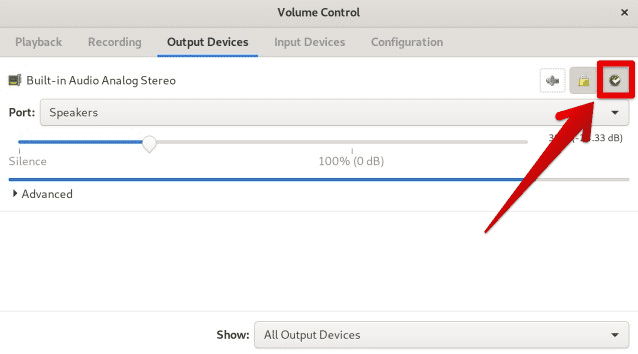
Setting a default output device
Note: Some applications may override the default output device and use their own audio settings. To ensure that the default output device is used consistently, adjust the audio settings within individual applications.
Configuring default input devices
In addition to setting the default output device, PulseAudio allows you to set a default input device for audio recording. To configure the default input device, you first need to identify the available input devices on your system.
Open the “PulseAudio Volume Control” application to identify the available input devices. Click on the “Input Devices” tab to view a list of available devices. You should see a list such as “Internal Microphone”, “External Microphone”, or other audio peripherals currently connected to your system.
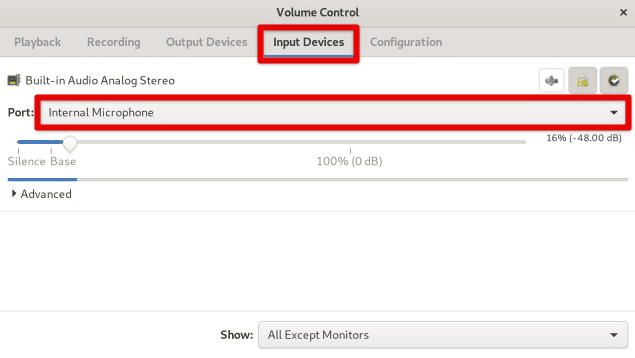
PulseAudio volume control input devices
To set the default input device, click on the green checkmark icon next to the device you want to set as the default. Doing so marks that device, and audio will be automatically recorded from this device unless specified otherwise. You can also adjust each device’s volume level, and balance with the provided sliders.
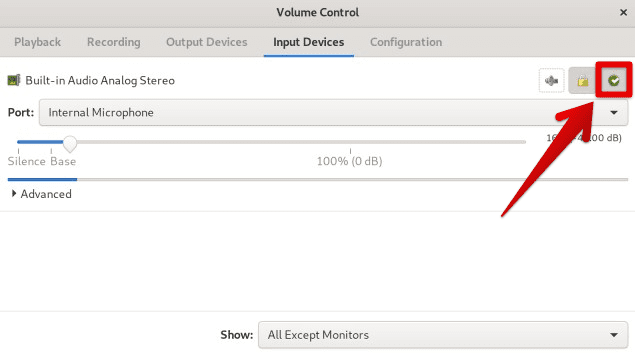
Setting a default input device
Note: Some applications may override the default input device and use their own audio settings. To ensure that the default input device is used consistently, adjust the audio settings within individual applications.
Managing volume levels
In addition to configuring the default input and output devices, PulseAudio also provides a way to manage volume levels for devices and individual apps. To adjust the volume of the default input or output device, open the “PulseAudio Volume Control” application and click on the “Output Devices” or “Input Devices” tab, depending on what you want to adjust.
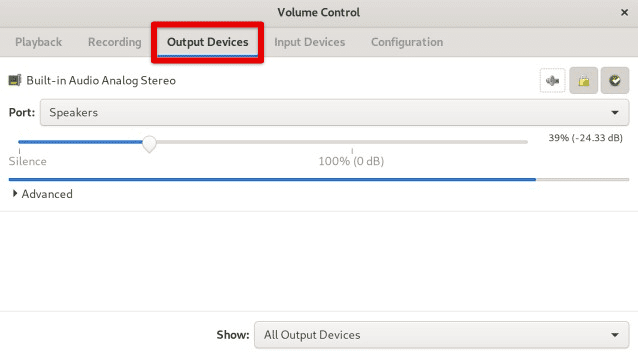
Accessing output devices in the volume control
Find the device you want to manage, and use the slider to increase or decrease the volume. You can also adjust the balance between the left and right channels for stereo devices.
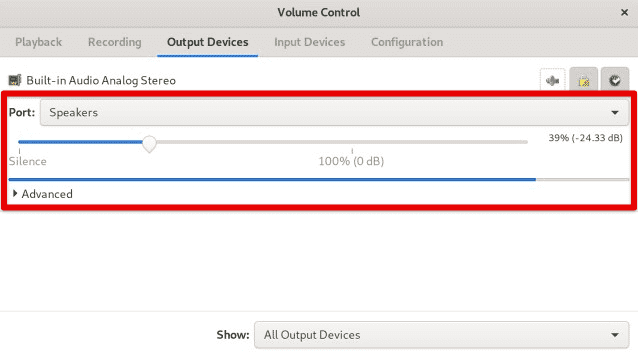
Adjusting volume level with sliders
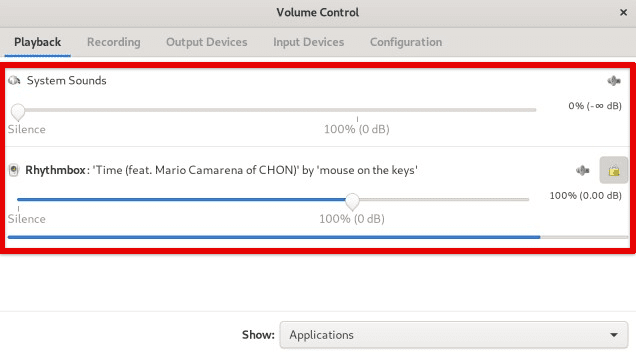
To control the volume of individual applications, open the “Playback” or “Recording” tab in the “PulseAudio Volume Control” application. There is a list of applications that are currently playing or recording audio. Use the sliders to adjust the volume for each application. It is also possible to mute individual apps by clicking the speaker icon next to the application name.

Adjusting volume level for applications
In addition to the graphical interface, PulseAudio also provides a command-line tool called “pactl” that can be used to manage volume levels. To increase the volume of the default output device by 10%, you can run the following command:
pactl -- set-sink-volume 0 +10%
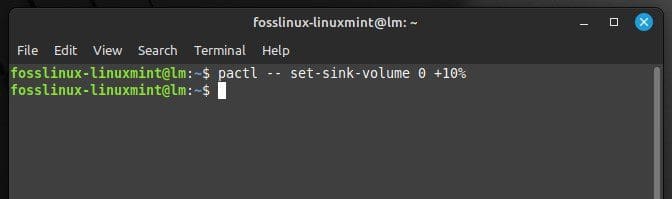
Increasing the volume level for the default output device
An audio editing software helps you edit audio into music by rearranging sounds, melody, harmony, and rhythm elements. Here are the top 14 open source audio editors for Linux.
Advanced configurations
While the basic configurations of PulseAudio in Linux Mint should be sufficient for most users, more advanced options are available for those requiring more customization and flexibility.
One advanced configuration is setting up a networked PulseAudio server. This allows you to play audio from one computer on another computer’s speakers. To set up a networked PulseAudio server, you must configure both the server and client computers to use the networked audio device. This can be done through the “PulseAudio Volume Control” application or by editing, configuration files manually.
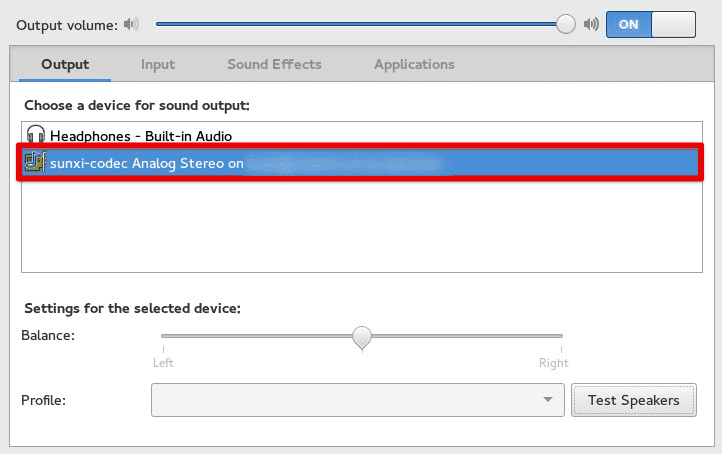
Networked PulseAudio server
Another advanced option is to configure sound effects. PulseAudio allows you to add sound effects to your audio output, such as adjusting the bass or treble levels or adding reverb. To configure sound effects, use the “PulseAudio Equalizer” application, which provides an intuitive menu for adjusting these sound settings. Alternatively, you can configure sound effects using the “pactl” command in the terminal.
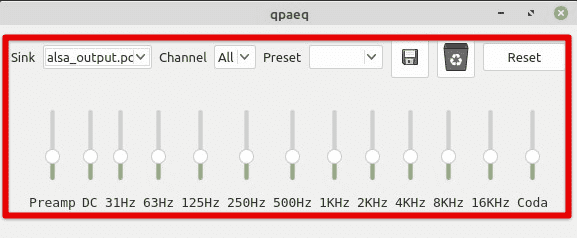
PulseAudio equalizer
Managing equalizer settings is yet another advanced configuration in PulseAudio. The “PulseAudio Equalizer” allows you to adjust the equalizer settings for the audio output, such as changing the gain levels for different frequency ranges. This can be especially useful for users who need to customize their audio output for specific music genres or listening environments.
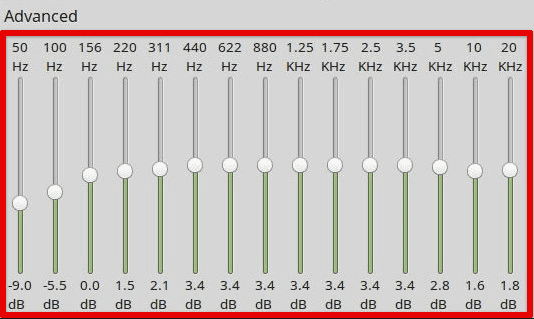
Adjusting gain levels
As described earlier, while the basic configurations should be sufficient for most users, advanced configurations, including networked audio, sound effects, and equalizer settings, are helpful for those who require more customization options.
Integrating with other applications
PulseAudio can be easily integrated with other applications on Linux Mint, such as Skype, Discord, or music players. By configuring these applications to use PulseAudio, one ensures that the audio output is consistent with the settings configured in PulseAudio.
To configure an application to use PulseAudio, you must install it locally on your system. Once the application is installed, open the “PulseAudio Volume Control” application and navigate to the “Playback” or “Recording” tab.
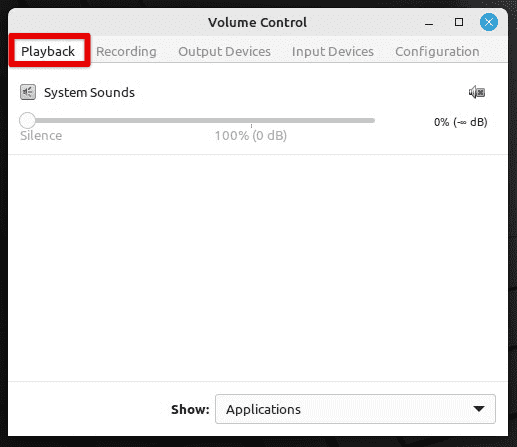
PulseAudio playback tab
Then, start the application and play some audio or start recording, and the application should appear in the list of applications in the “Volume Control”.
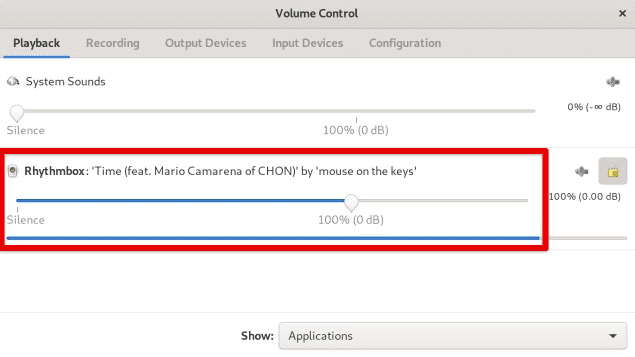
Applications in volume control
If the application does not appear in the list, manually configure it to use PulseAudio. This can typically be done through the application’s settings, which may allow you to select PulseAudio as the audio output or input device.
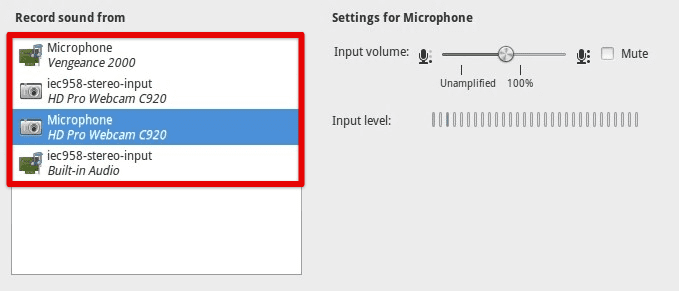
Configuring to use PulseAudio manually
In some cases, additional settings may be required to ensure the application uses PulseAudio correctly. Some music players might need you to configure the output plugin to use PulseAudio or to select the correct audio device in the settings menu.
Conclusion
Configuring PulseAudio in Linux Mint can significantly improve your audio experience and give you greater control over these settings. By following the steps outlined in this article, you can easily configure default output and input devices, manage volume levels, and even integrate PulseAudio with other applications.
We also covered advanced configurations such as setting up a networked PulseAudio server, configuring sound effects, and managing equalizer settings. With flexible configurations and an intuitive interface, you can easily employ PulseAudio to fine-tune audio settings in specific use cases. Linux Mint may encounter issues affecting its performance and day-to-day functionality like other operating systems. Go through our detailed guide on troubleshooting common Linux Mint issues.

1 comment
I JUST WANT TO SET SAMPLE RATE
IMPOSSIBLE