There are instances where you may need to write out long commands or sentences obtained from files on your browser while working on your Ubuntu terminal. This will most definitely be so tedious to type word by word but wait! You can save your precious time by using copy-pasting techniques.
Using the standard keyboard command shortcuts Ctlr+c and Ctrl+v, you would have copied and pasted multiple times in your Linux Graphical User Interface(GUI) apps like OpenOffice, LibreOffice, Gedit, and more. But to your surprise, you may have noticed that the same command shortcuts don’t work in the Linux terminal.
Copy and Paste from the command line in the Linux Terminal
And that is where this article will focus more. This guide will use two methods to copy-paste data in the Linux terminal. The executed examples in this guide were on Ubuntu 22.04; Let us get underway.
Method 1: How to copy-paste on a Linux terminal using the right-click context menu
In this approach, you will have to use the mouse to highlight the text; why not use it to copy and paste? You can use the mouse to right-click to copy-paste in other Linux apps. For this situation, usually select the text you want to copy; after that, hit the right mouse button, and you will be dispensed with the context menu with several options. Go ahead and click on the “Copy” option. You can paste this command to any script, terminal window, or any other document of your liking. Look at the following instance:
Instance 1: In the following instance, we will copy-paste the command executed in the Linux terminal to a document called “fosslinuxtuts”:
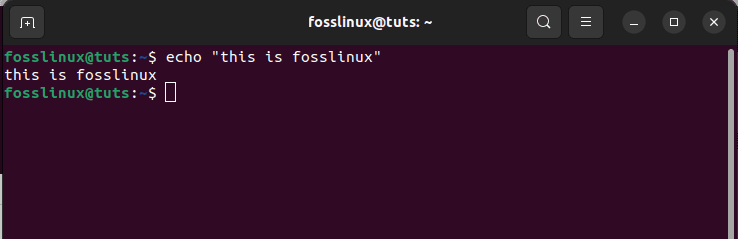
Copy-paste the command
First, we will select the entire command. After that, use the right-mouse button context menu and opt for the “Copy” option as highlighted below:
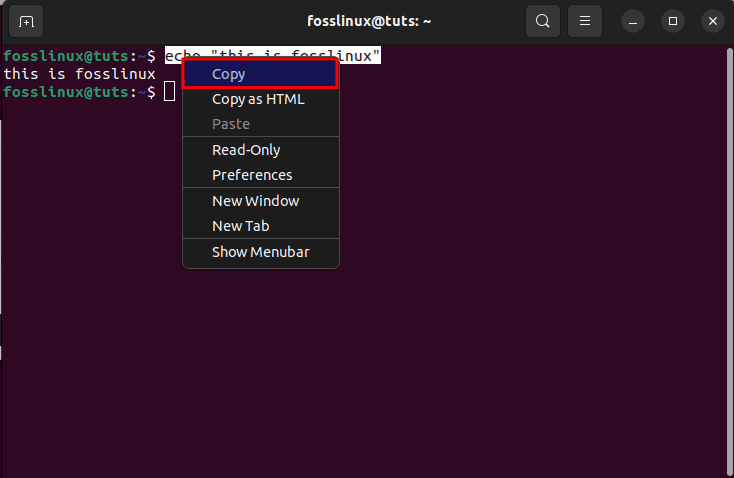
select copy
Now that we have copied the command, we will proceed further and paste the copied command into our “fosslinuxtuts” document. Open your document (preferred position to paste) and click on the document’s position where you want to place the copied command, and then from the right-click context menu, click on the “Paste” option as shown below:
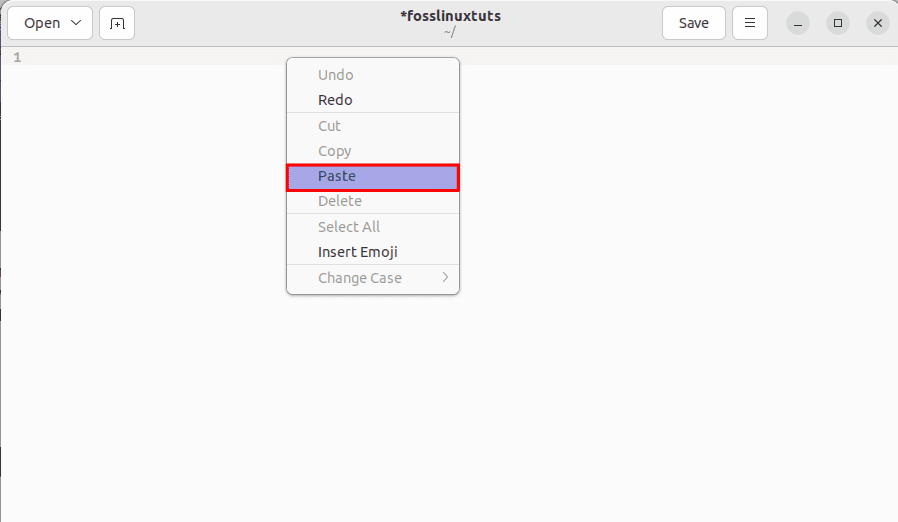
select paste
And the snapshot below clearly shows that the process was successful.
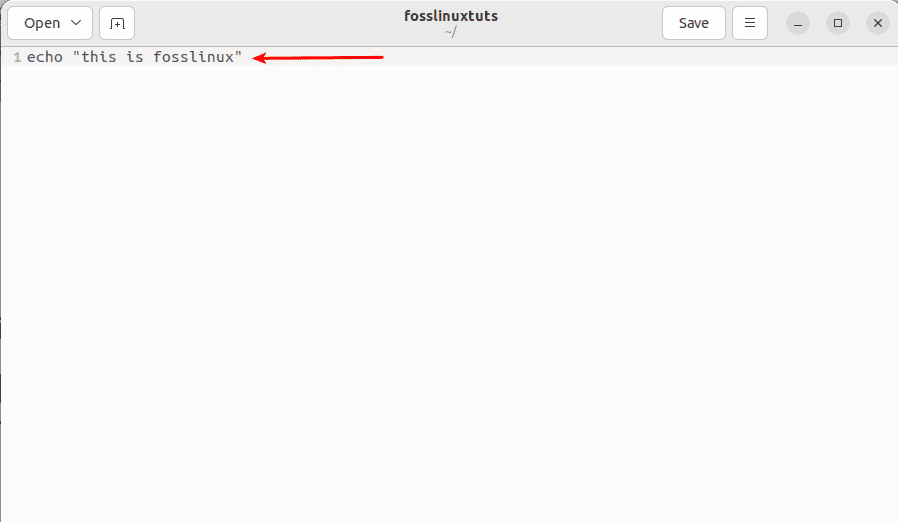
pasted text
Instance 2: In Linux, in this case, Ubuntu, you can use your mouse’s context menu and right-click to copy-paste from a terminal to the other terminal window. In such cases, select the command or text you want to copy and click on the “Copy” option as demonstrated below:
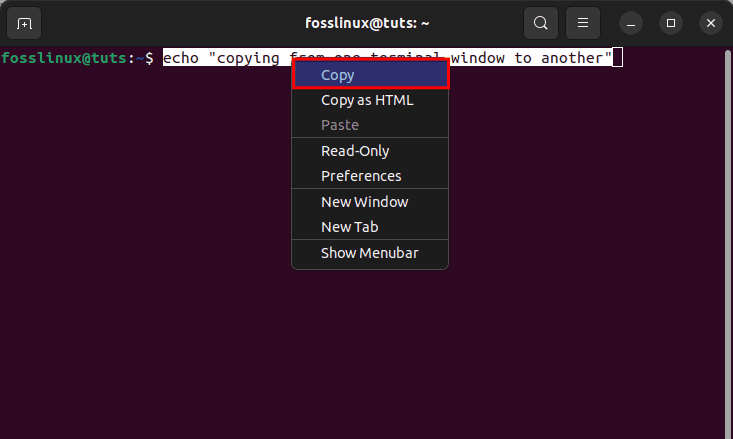
Copy from one terminal to another
Next, navigate to the other terminal and paste the selected command in the following manner:
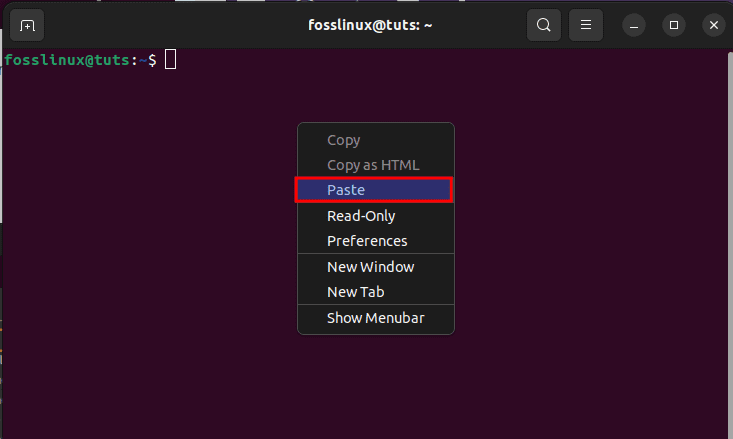
Paste the newly copied text
Final output:
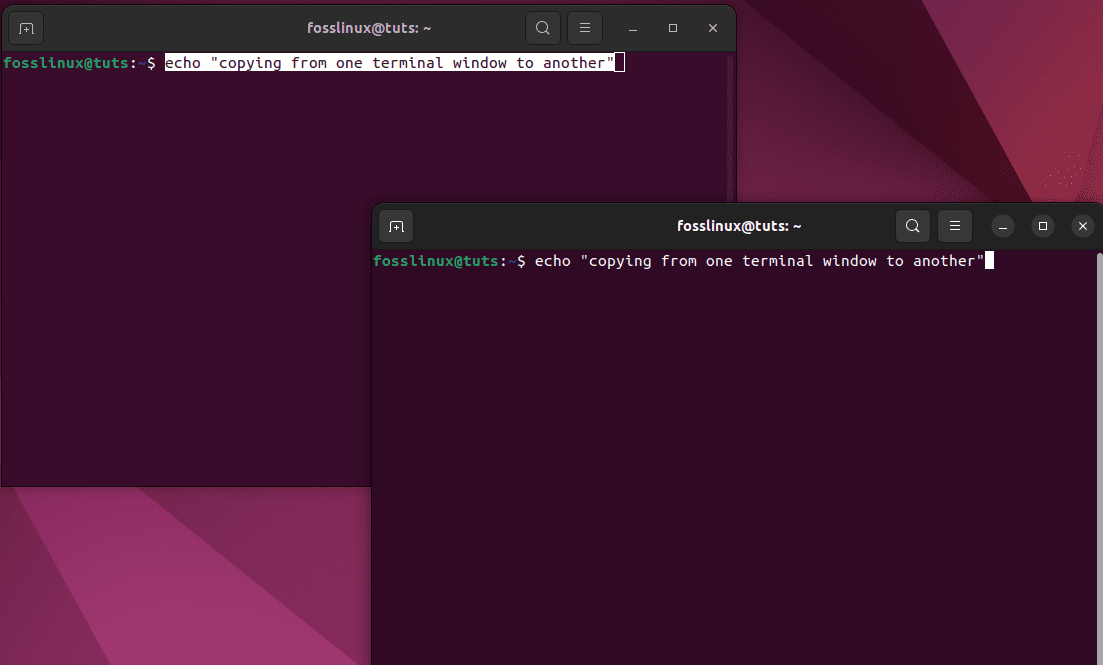
final output
And all should be done!
Next, let us also see how we can do the same using keyboard shortcuts.
Method 2: How to copy-paste on the Ubuntu terminal using keyboard shortcuts
Most, if not all, PC users are accustomed to using the “Ctrl+c” and “Ctrl+v” for copying and pasting, respectively. These shortcuts also work on the Linux desktop but not on the terminal. We have to append the “shift” key in these keyboard shortcuts to copy or paste commands to or from the Linux terminal.
The directives are pretty straightforward:
- To copy a command or text from the Linux terminal, hit the “Ctrl+shift+c.”
- To paste a command or text in the Linux terminal, hit the “Ctrl+shift+v.”
- Press “Ctrl+c” to copy text or command at any point besides the Linux terminal.
- Press “Ctrl+v” to paste text or command in any document or script.
Let us look at some relevant examples:
Instance 1: In the example given below, we will be trying to copy commands from the document “fosslinuxtuts” to our Ubuntu terminal:
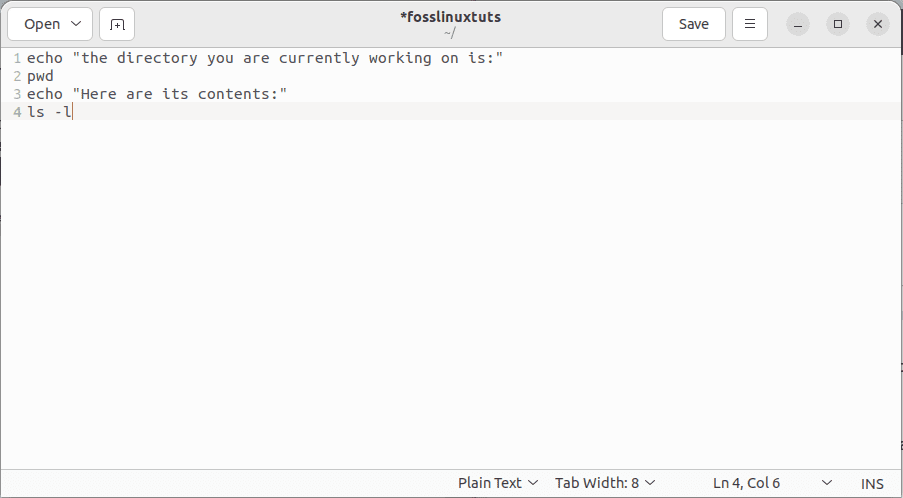
Copy files from fosslinuxtuts
First things first, select all the required commands or texts for copying and then press “Ctrl+c”:
select everything
After that, navigate to your terminal window and paste the commands or texts in it by hitting the “Ctrl+shift+v”:
press Ctrl+shift+v
The above operation will paste and execute the copied commands in the console simultaneously, as shown in the snapshot below:
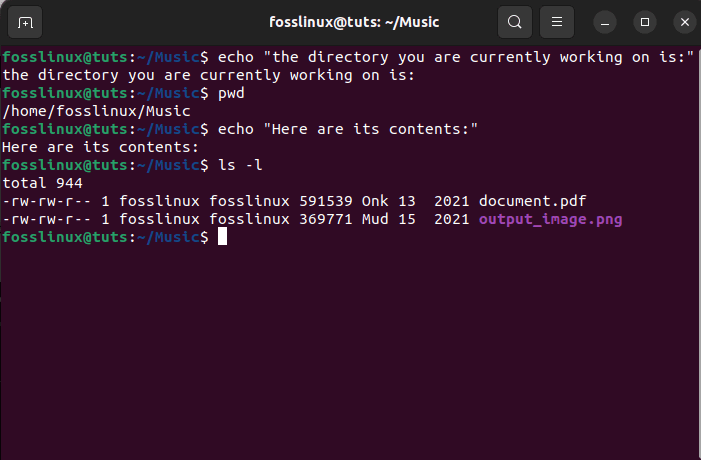
paste simultaneously
Note: The command will be executed immediately if you paste the command or text into the Ubuntu terminal with a trailing newline. The simplest way to avoid these situations is by clicking at the end of the text or command and dragging it to the beginning. This selection method will be able to copy commands which will later be pasted into the Linux terminal without executing them instantly, as shown below:
First, select the text from the document by using the method mentioned above. After that, press “Ctrl+c” to copy it:
Copy from document
Maneuver to your Linux terminal and hit the “Ctrl+Shift+v” to paste the copied command:
press Ctrl+shift+v
The snapshot below displays that we have successfully pasted the text from our “fosslinuxtuts” document to the terminal without executing it instantly.
echo from another document
Instance 2: How to copy-paste from the Linux terminal to a document using keyboard shortcuts
To copy-paste, any command from the terminal window, select it by pointing the cursor at the end of it. After that, use the mouse left-click button and drag it towards the start of the command. Once you have selected the command, hit the “Ctrl+shift+c” to copy it.
press ctrl+shift+c
Next, open up the document(your preferred destination) where you want to paste the command and press “Ctrl+v.” And now, the “fosslinux” document will look like this:
Press ctrl+v
Here is why there are no universal key shortcuts for copy-paste in the Linux terminal.
The keybindings for copy-pasting depend on the console emulator (commonly known as the terminal). If you weren’t aware, a terminal is just an app, and you can also set up other terminals like Terminator or Guake.
Diverse terminal apps may have keybindings for copying and pasting, like “Alt+C/V or “Ctrl+Alt+C/V.”
Most terminals utilize the “Ctrl+Shift+C/V” keys for copying-pasting. Still, if it doesn’t work for you, you may check out other key combinations or configure the keys from the preferences of your terminal emulator.
Why do Linux terminals not use the “universal” Ctrl+C and Ctrl+V
No Linux console will provide the “Ctrl+C” for copying text. This is considering that, by default, “Ctrl+C” sends an interrupt signal to the command running in the foreground. This usually stops the running command, as shown in the snapshot below:
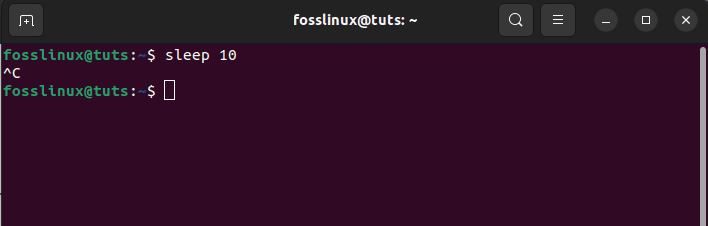
Terminal does not use Ctrl+C
This behavior existed way before “Ctrl+C and Ctrl+V” started being used to copy-pasting text. A point worth noting is that since the Ctrl+C is reserved for stopping a command, it cannot be used for copying.
Now let us change our focus and see how we can copy-paste a single file using the terminal in Linux.
How to copy and paste a single file
This section will use the cp command whenever we want to copy a file or folder in the Linux command line because the afore keyboard shortcuts won’t work. The cp command is a shorthand for copy. The syntax is pretty straightforward. To do this, we will use the cp command followed by the file you want to copy and the destination where you want it moved.
cp your-file.txt ~/destination/
Where:
cp ~/foss_linux.txt ~/Documents/
This command tells our system to copy a file by the name “foss_linux.txt” from the home folder and move it to the Documents folder.
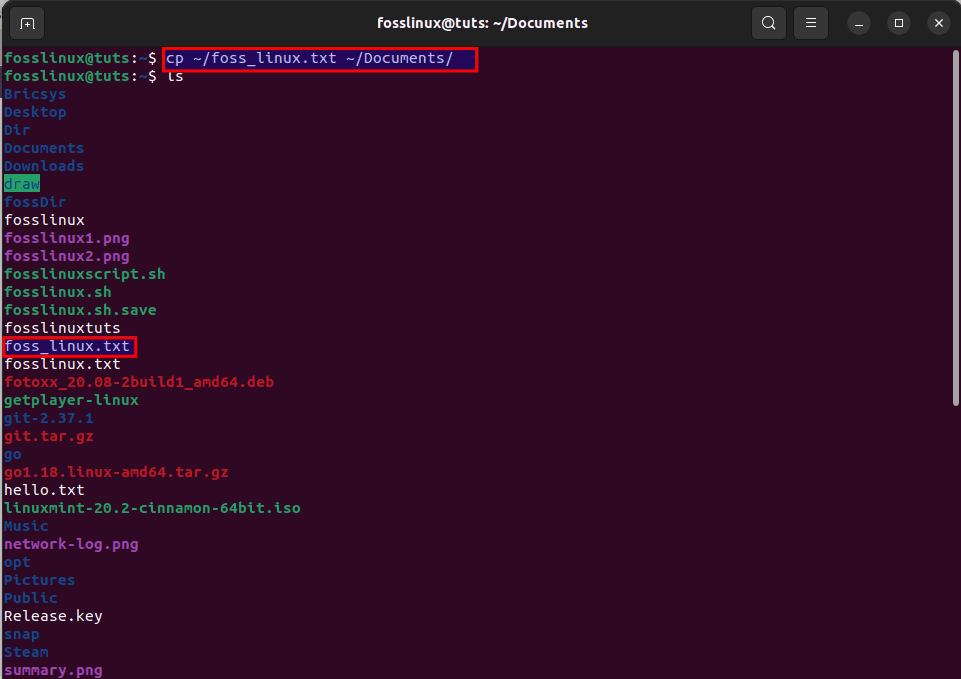
Copy file
Then check the destination:
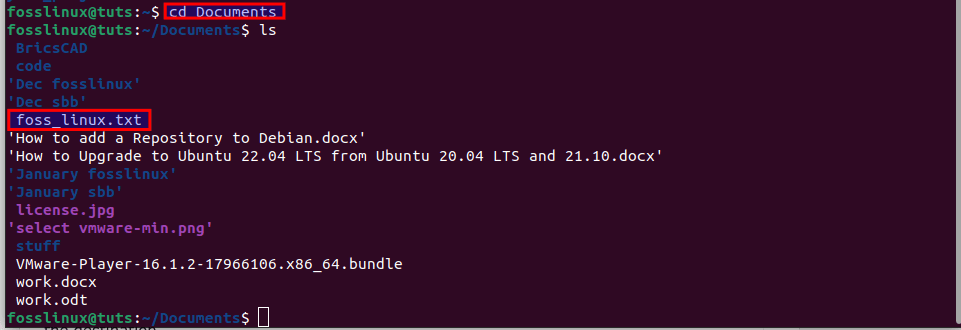
Check the destination
The above sample presumes that your file(foss_linux.txt) is in a corresponding directory(home directory) you are working out of. However, that does not limit you from specifying both using the following syntax:
cp ~/Downloads/your-file.txt ~/Documents/
You can also rename your file while copying it. To do this, you will specify the new name in the destination section.
cp ~/Downloads/your-file.txt ~/Documents/new-name.txt
First, list the destination of the file to rename as highlighted below:
ls
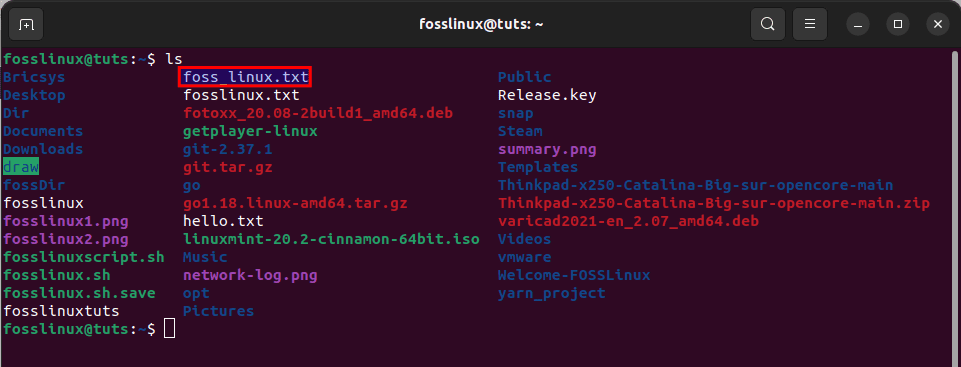
initial file
Then rename it as shown below:
cp ~/foss_linux.txt ~/Documents/fosslinuxtutorials.txt
In the end, you can list the files to see if your intended file has picked the changes or not:
ls
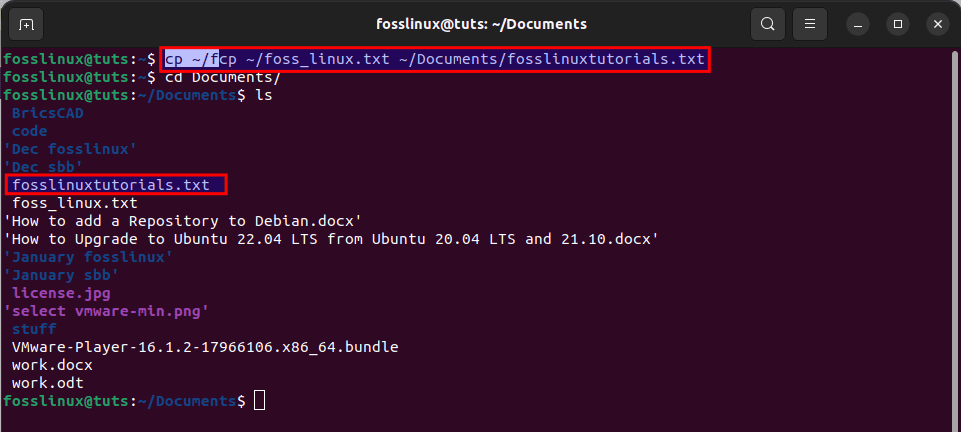
renamed
Now let us look at how we can copy and paste a folder and its contents.
How to copy and paste a folder and its contents
To copy a folder and its contents, you must tell the cp command to copy recursively. That is simple enough with the -r flag, which follows the following syntax:
cp -r ~/Directory/folder ~/new_destination
Where:
cd Pictures ls cp -r ~/Pictures/CAD ~/Documents cd Documents ls
This command tells our system to go to the Pictures directory. After that, list the contents of the pictures directory, then run the command, which will copy a folder named CAD in the pictures directory and paste it into the Documents location, and finally list the Pictures directory once again to see if the CAD folder is moved as shown in the snapshot below:
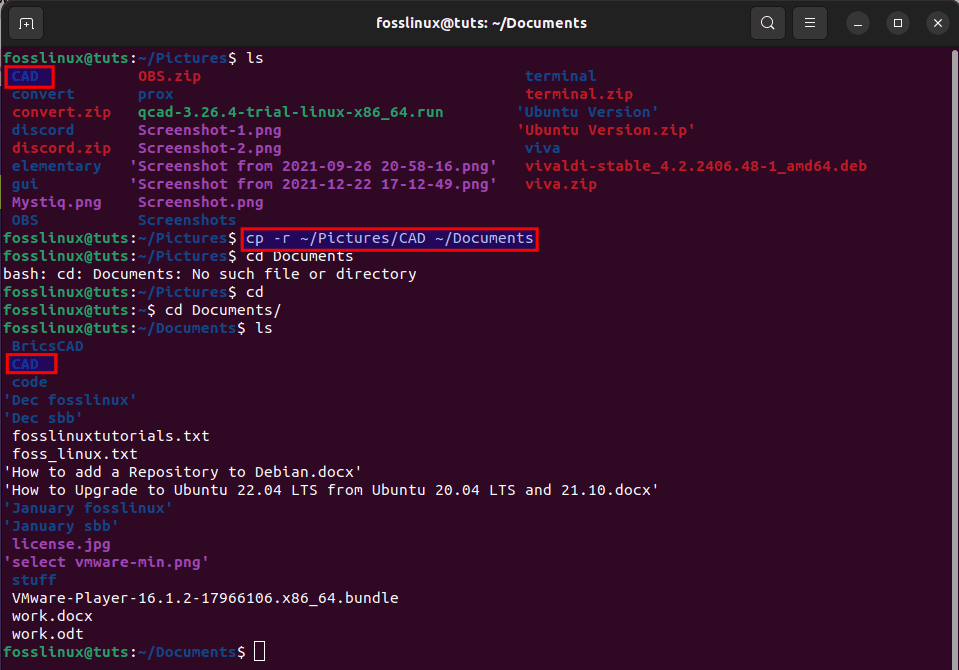
copy folder
All of the other syntaxes are precisely the same. The -r flag tells the cp that it works with a directory and should copy its contents.
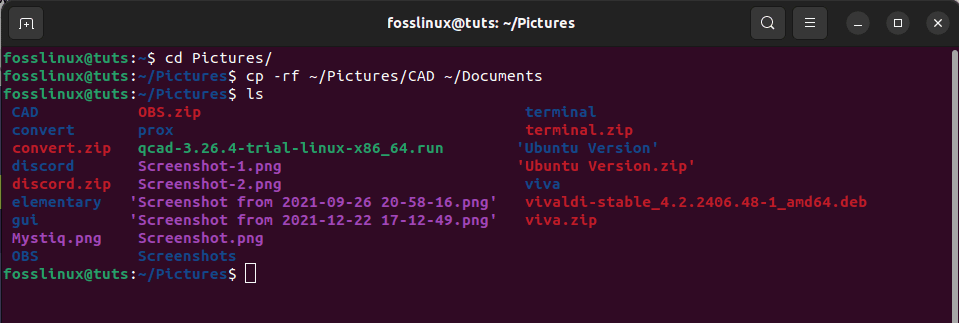
On the condition that you want the paste action to overwrite existing files, you can append the -f flag:
cp -rf ~/Directory/folder ~/new_destination
Where:
cp -rf ~/Pictures/CAD ~/Documents
overwrite
Finally, let us see how we can copy-paste multiple files.
How to copy-paste multiple files in Linux using the terminal
It isn’t a big deal to copy and paste multiple files in Linux using the terminal. The Linux command line allows you to target multiple items simultaneously with {}. The curly brackets are used to list the names of every file that is to be copied, after which you will separate them by commas, as shown below:
cp ~/Downloads/{file1.txt,file2.jpg,file3.odt} ~/Documents/
Where:
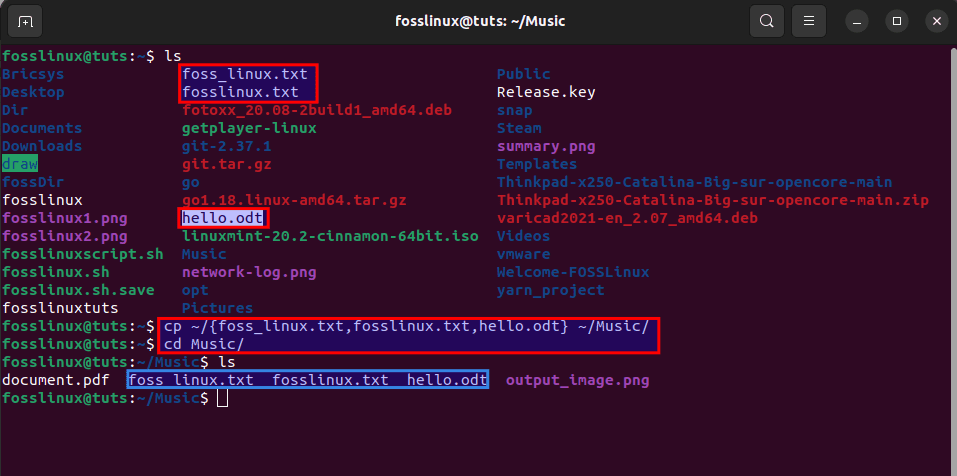
cp ~/{foss_linux.txt,fosslinux.txt,hello.odt} ~/Music/
cd Music
ls
The above command copies files (foss_linux.txt,fosslinux.txt, and hello.odt) from the home folder and moves them to the music folder, as shown by the following procedure.
Copy-paste multiple files
Terminal Copy-Paste Keyboard Shortcuts
| Keyboard Shortcut | What it does? |
|---|---|
| Ctrl+Shift+c | Copy selected text |
| Ctrl+Shift+v | Paste copied text |
| Ctrl+u | Cut everything from line start to cursor |
| Ctrl+k | Cut everything from the cursor to end of the line |
| Alt+d | Cut the current word after the cursor |
| Ctrl+w | Cut the current word before the cursor |
| Ctrl+y | Paste the previous cut text |
| Alt+y | Paste the second latest cut text |
| Alt+Ctrl+y | Paste the first argument of the previous command |
And there you have it!
Final Thoughts
There are always options to copy and paste data in the Ubuntu terminal whenever you want to reuse any text. In Linux, copy-paste enables you to copy and paste text commands without retyping them repeatedly. This process saves you lots of precious time that was to be lost on an effortless task.
This guide has covered two different approaches to copy-paste commands in your Linux. We also showed how to copy and paste a single file, copy and paste a folder and its contents, and copy-paste multiple files in Linux using the terminal. From our end, we suggest using the keyboard shortcuts for copy-paste than using the right-click menu. You can also tour how you can disable unsafe copy-paste warnings while using a terminal in elementary OS. We hope this was educative enough; otherwise, keep following FOSSLinux for more tips.


3 comments
I am Linux Beginner and I found the article useful. Great Job. : )
its useful for beginner
shift insert