Many issues, including hardware incompatibilities, corrupted system files, or incorrect configurations, can cause boot problems in Linux Mint. These problems can lead to slow boot times, boot failures, or even a complete inability to boot the system. Boot problems can be frustrating and disrupt your workflow, but fortunately, many of these issues can be resolved with basic troubleshooting. In this blog post, we will discuss some of the most common causes of boot problems in Linux Mint and provide step-by-step solutions to help you diagnose and fix these issues.
Boot woes no more: Fixing Boot problems in Linux Mint
Step 1: Check your BIOS settings
The BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) is a firmware interface that controls your computer’s hardware. When you start your computer, the BIOS is the first software that runs, and it performs a series of checks to ensure that your hardware is working correctly before passing control over to your operating system. If your BIOS settings are incorrect or corrupted, this can cause boot problems in Linux Mint.
You will need to access the BIOS setup utility to check your BIOS settings. The method for accessing the BIOS can vary depending on your computer’s manufacturer. Still, you can typically access it by pressing a key during the boot process, such as F2 or Del. Once you are in the BIOS setup utility, navigate to the Boot tab or menu and ensure your hard drive is listed as the first boot device. If your hard drive is not listed, you may need to check the connections or replace it with a new one.
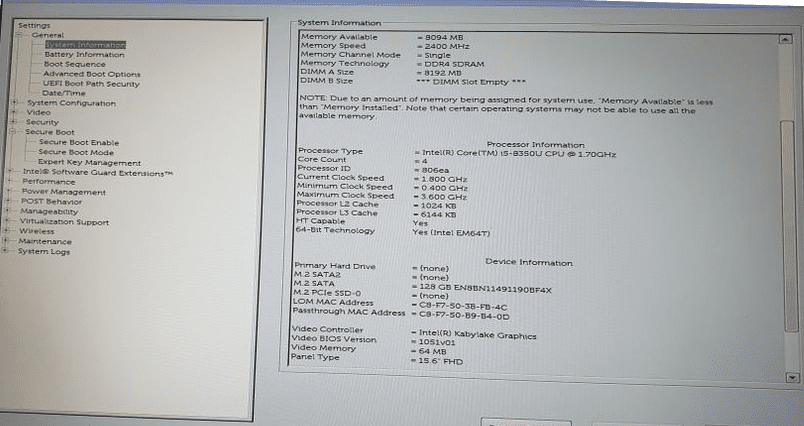
Dell BIOS/UEFI setup screen
You should also check the Secure Boot setting in your BIOS. Secure Boot is a feature that prevents the system from booting from unauthorized sources, such as a bootable USB drive. While Secure Boot can enhance security, it can cause boot problems if misconfigured. Make sure that Secure Boot is set to either “Disabled” or “Legacy Mode” in your BIOS settings.
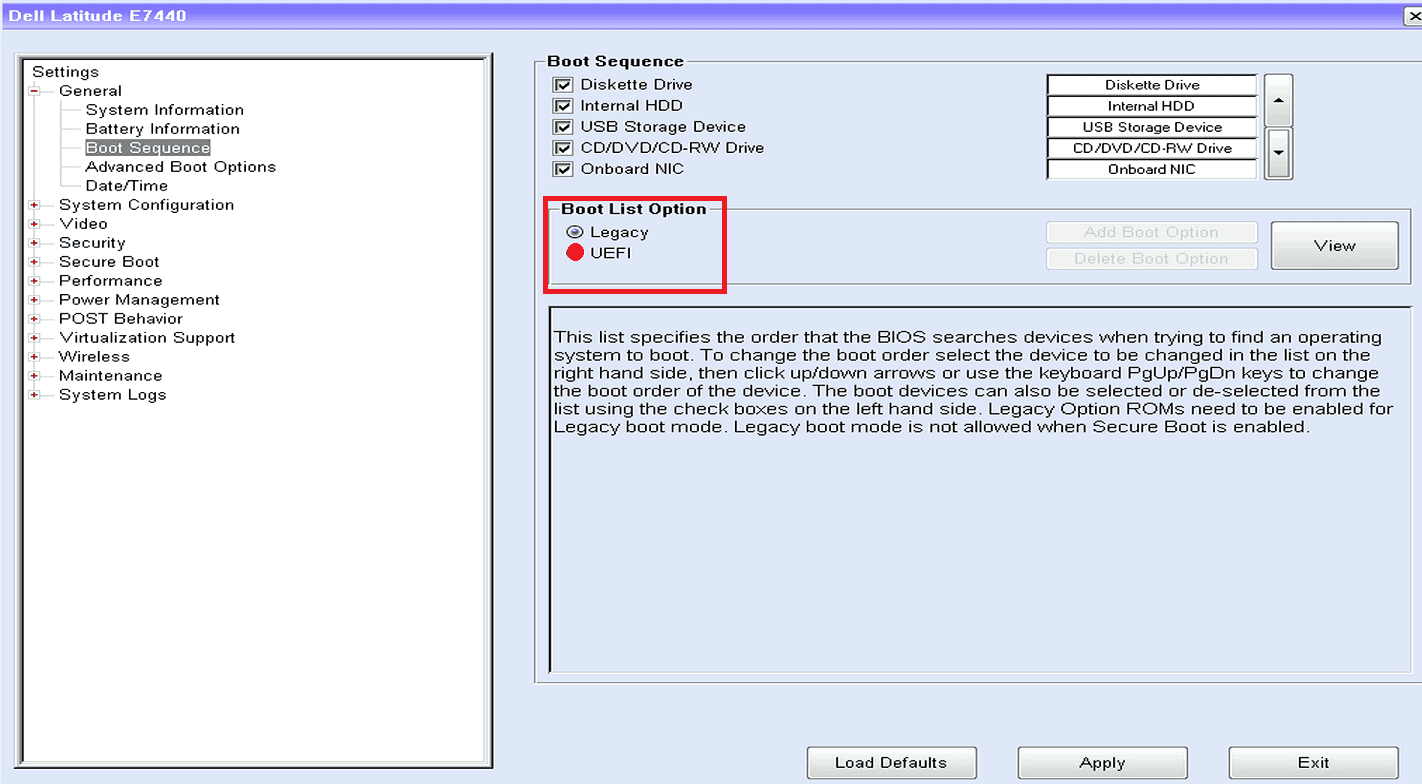
UEFI/BIOS Boot select screen
Once you have made any necessary changes to your BIOS settings, save your changes and exit the BIOS setup utility. Then, restart your computer and check if the boot problem has been resolved. If the issue persists, you may need to try other troubleshooting steps, such as running a file system check or reinstalling your bootloader.
Step 2: Run a file system check
If your BIOS settings are correct, the next step is to run a file system check. This will help identify any corrupted files that may be causing the boot problem.
The file system check, or fsck, is a utility that checks and repairs file system errors. These errors can occur for various reasons, such as power outages or hardware failures, and can cause boot problems in Linux Mint.
To run a file system check, you must boot into recovery mode. To do this, restart your computer and hold down the Shift key while the system is booting. This will bring up the GRUB menu, allowing you to boot into recovery mode. Once you have booted into recovery mode, select the option to run a file system check.
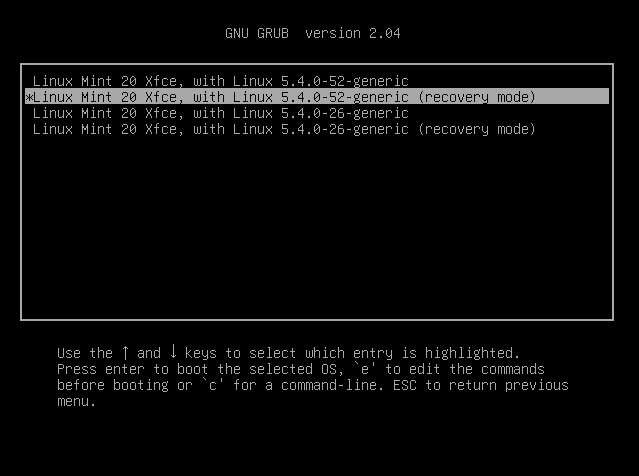
Linux Mint recovery issues
The file system check will scan your hard drive for errors and attempt to repair any issues it finds. This process can take some time, depending on the size of your hard drive and the number of errors detected. Once the file system check is complete, you can reboot your system and see if the boot problem has been resolved.
If the file system check does not resolve the boot problem, you may need to try other troubleshooting steps, such as reinstalling your bootloader or checking for hardware issues. Nevertheless, running a file system check should be a routine part of system maintenance, as it can help prevent file system errors and other issues that can cause boot problems in the future.
Step 3: Reinstall your boot loader
The boot loader is a small program that loads the operating system into memory and starts it running. If the boot loader is corrupted or missing, this can cause boot problems in Linux Mint. Reinstalling the bootloader can fix this issue and get your system booting again.
To reinstall the bootloader, you must boot from a Linux Mint Live USB or CD/DVD. Once you have booted from the Live media, open a terminal and enter the following command:
sudo fdisk -l
This command will display a list of your hard drives and partitions. Note the partition number of your Linux Mint installation.
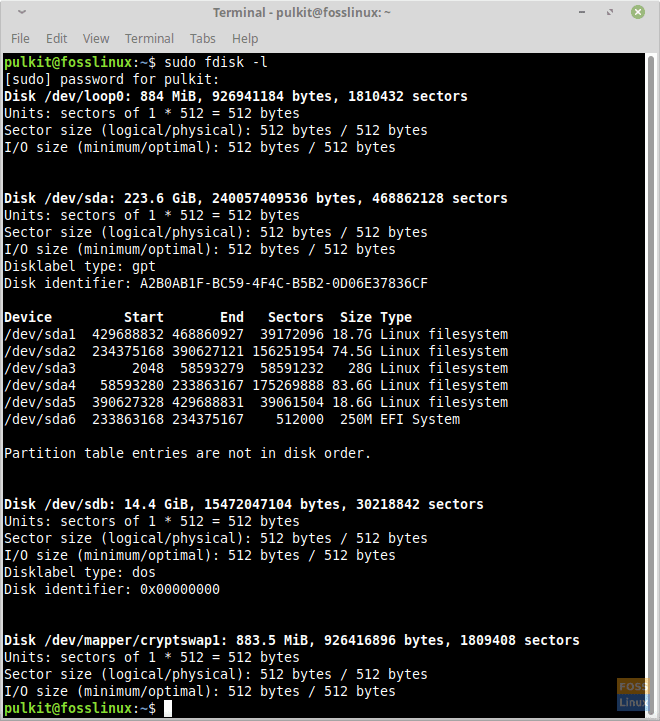
fdisk -l on Linux Mint.
Next, mount the Linux Mint partition by entering the following command, replacing “sdaX” with the partition number you noted earlier:
sudo mount /dev/sdaX /mnt
Once the partition is mounted, you need to chroot into the Linux Mint installation by entering the following command:
sudo chroot /mnt
This will allow you to run commands as if you were booted into the Linux Mint installation.
Now, you can reinstall the boot loader by entering the following command:
For BIOS systems:
sudo grub-install /dev/sda
For UEFI systems:
sudo grub-install --target=x86_64-efi --efi-directory=/boot/efi --bootloader-id=linuxmint --recheck --no-floppy
Once the installation is complete, update the grub configuration by entering the following command:
sudo update-grub
Exit the chroot environment by entering the following command:
exit
Unmount the partition by entering the following command:
sudo umount /mnt
Restart your computer and check if the boot problem has been resolved. Reinstalling the bootloader can be a complex process, so follow these steps carefully and make backups of your important data before proceeding.
Step 4: Check for hardware issues
If none of the previous steps have resolved the boot problem, it’s possible that there could be a hardware issue causing the problem. Checking for hardware issues involves running diagnostics on your computer’s hardware components to determine if any issues could be causing the boot problem.
Here are some steps you can take to check for hardware issues:
First, check the hard drive: A failing hard drive can cause boot problems. Next, use a SMART (Self-Monitoring, Analysis, and Reporting Technology) diagnostic tool to check your hard drive’s health. You can use tools like GSmartControl or smartmontools to check your hard drive’s SMART status and run diagnostics.
Check the memory: Faulty RAM modules can also cause boot problems. You can use the built-in memory diagnostic tool in Linux Mint to check for memory errors. To access the memory diagnostic tool, reboot your system and hold down the Shift key to access the GRUB menu. Then, select the option to run a memory test.
Check other hardware components: Other components, such as the CPU or motherboard, can cause boot problems. To test other hardware components, you can run hardware diagnostics using tools like memtest86+ or StressLinux.
If the hardware diagnostic tools indicate a problem with a hardware component, you may need to replace the component to resolve the boot problem. But, again, it’s best to consult a professional or hardware manufacturer to determine the best course of action.
Conclusion
Boot problems in Linux Mint can be frustrating, but there are several steps you can take to diagnose and fix them. Checking the BIOS settings, running a system check, reinstalling the boot loader, and checking for hardware issues are all effective ways to troubleshoot and resolve boot problems in Linux Mint. Remember to make backups of your important data before attempting any fixes and proceed cautiously, especially when dealing with complex solutions like reinstalling the bootloader or checking for hardware issues.


4 comments
I agree, Secure boot is far more useful running a Windows only install then either a solo Linux or duel boot Windows/Linux install. I have always felt it wasn’t needed at all in a purely Linux install and may actually cause more grief then any potential security advantage. Windows just is a complete security mess and a huge target and no security will stop attacks or discourage hackers from trying. They always seem to find a way into a Windows system.
I keep falling at the chroot step.
I get this error message:
chroot: failed to run command ‘/bin/bash’: No such file or directory but file does exist
Your “Newsletter Subscribe” button is not working in my Firefox browser. Are your newsletters no longer available?
Thank you for bringing this to our attention. I’m pleased to inform you that we have addressed the issue with the “Newsletter Subscribe” button and it should now be functioning correctly in the Firefox browser. Our newsletters are indeed still available, and we encourage you to try subscribing again.
If you continue to encounter any problems or have further questions, please don’t hesitate to reach out. We appreciate your interest in our content and apologize for any inconvenience caused.